In-depth Transmission Parts: Delve into the intricacies of transmission parts, understanding the role of key components such as clutch, gearbox, driveshaft, and electronic control modules. Learn how these components contribute to efficient and smooth vehicle propulsion, combining mechanical finesse with technological advancements.
In any vehicle, Parts in Transmission are the important bridge connecting the power from the engine to the wheels, making it possible to move and control. Without an efficient transmission system, a vehicle would not be able to change speed or power output as per driving conditions. While these components are often taken for granted, they are essential for performance, fuel economy, and safety of the vehicle. This comprehensive guide seeks to unveil the intricacies of automotive transmission components, demystifying their distinct roles, interplay, and technological advancements. Whether you’re an automotive enthusiast, an engineering student, or a vehicle owner looking to understand the inner workings of your ride, these components are essential to understanding the evolution of vehicles and how they work.
The Bottom Line: What Are Parts in Transmission?
The transmission system can be described as the soul of the drivetrain, which is responsible for transferring the power produced by the engine to the wheel in a controlled manner. This intricate system encompasses different parts, including the clutch, gearbox, driveshaft, differential, and in modern vehicles, electronic control modules and sensors. Traditional transmissions are mechanical in nature, using a series of interlocking gears and shafts to vary speed and torque. However, modern designs combine these hydraulic, electronic, and even computerized elements to provide smooth gear shifting and optimal performance.
In simple terms the transmission modulates engine power to varying driving conditions. At low speeds or when climbing, more torque is needed, whereas at cruising speeds lower torque and higher gear ratios conserve fuel. The components of transmissions cooperate to meet these various requirements effectively.
Thorough Examination of Key Transmission Parts
 The Clutch: The Gateway to Power Activation
The Clutch: The Gateway to Power Activation
The clutch is the important part of the interface between the engine and the transmission system, particularly the manual car. It is mainly composed of clutch disc, pressure plate and release bearing. The clutch works to engage and disengage the power of the engine to the transmission to help drivers shift gears without grinding. When the clutch pedal is depressed, the friction engagement is disengaged which allows for a gear change, then when the pedal is released, the friction engagement returns smoothly allowing power to flow through the drivetrain. The clutch provides a way for the engine to spin when the vehicle is not moving, and to allow for smooth starts and stops. Slippage of the clutch or trouble with shifting gears indicate wear and the need for servicing or replacement.
Gearbox: The Key to Speed and Torque Control
The transmission, or as it’s called simply, the gearbox, houses a variety of gears that translate the engine’s revolutions into usable power that’s right for a variety of speeds and load conditions. Manual transmission: The driver must manually shift gears, offering precise control over the vehicle’s response and fuel economy. The internal gear ratios range widely to allow the driver to choose an appropriate gear for acceleration, cruising or climbing. Synchronizers of the gearbox help match gear-speed during gear changes, and avoid noisy clashes or mechanical damage.
Automatic transmissions, however, utilize planetary gear sets that integrate the gears in a compact system to achieve a variety of speed ratios in an automated fashion. These planetary gear boxes, along with hydraulic control systems and sensors, allow the gear shifts to be smooth and automatic without any input from the driver.
Universal Joints and Driving Shafts: The Power Transmitters
The driveshaft (or propeller shaft) is the shaft that connects the gearbox to the differential and then to the wheels. Especially in rear-wheel and four-wheel drive vehicles, it serves an inestimable function in torque transmission over a distance, while it can tolerate suspension travel and angular changes via universal joints. It needs to be able to take tremendous torque and rotational forces to be able to operate reliably. Without the right maintenance, you might experience some of the common symptoms of drive shaft problems like vibrations or noises during driving.
Differential: The Smooth Turns Enabler
When a vehicle turns the wheels roll different distances and so need to rotate at different speeds. The differential is placed between the driveshaft and the wheels and serves that purpose. By employing a set of precision gears (most commonly a ring and pinion), the differential splits engine torque for each wheel while permitting respective wheel speed differences to occur. This feature makes it easier to handle the vehicle, particularly on winding roads, and minimizes tire wear. Advanced differentials: High-performance differentials like limited-slip or electronically controlled differentials offer even more traction and performance on slick surfaces.
Torque Converter and Hydraulic Control circuits in Automobiles
In automatic transmissions the mechanical clutch is replaced by a torque converter. It is a fluid coupling device that will let the engine run when the vehicle is stopped without stalling. The torque converter is used to increase engine torque during acceleration, allowing the vehicle to move efficiently. Hydraulic systems utilize specialized transmission fluid under pressure supplied by pumps and valves that engage clutches and bands to adjust gear ratios without input from the driver. This system allows for seamless gear shifts, improved fuel efficiency, and ensures optimal performance in various driving conditions.
Transmission Control Units and Sensors: Electronics Integration
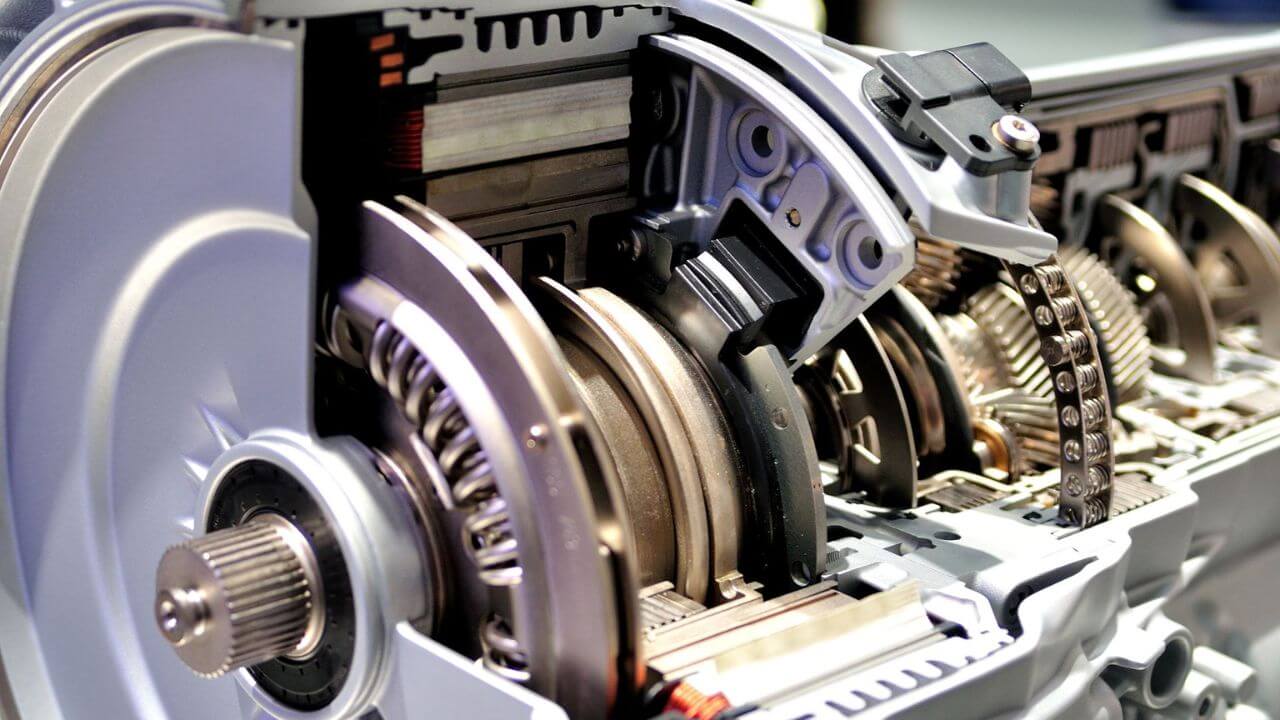
The Importance of Transmission Parts in Auto Engineering

Different components also play vital roles in the functioning of the vehicle, and understanding their functions is essential for proper vehicle maintenance and troubleshooting. For instance, identifying the early signs of clutch wear or fluid leakage can help avoid costly transmission repairs. Moreover, an understanding of transmission systems is critical to engineers who are extending the limits of fuel economy and performance in the hybrid and electric vehicle realm, which often incorporate new advanced transmission technologies or do away with conventional components altogether.
Theoretical research is focused on new materials and control algorithms for minimizing the transmission losses and enhancing the component reliability. The continuous research into the changing control processes and adaptive transmission strategies ensures the best possible optimization of the complex systems for specific driving situations, which are an example of the adaptation of transmission components to technological progress.
Results: Accepting the Complexity of Parts for Transmission
Transmission – The transmission is the core of every vehicle’s ability to move freely and efficiently. From the basic clutch and gear sets through to the latest torque converters and electronic control modules, the system is a true masterpiece of integrated mechanical and electronic engineering. By exploring these components, one develops an immense appreciation for the complex dynamics that not only facilitate daily transportation but continue to fuel the ever-evolving innovation that propels the automotive industry forward.
This comprehensive understanding equips drivers and professionals with the knowledge to appreciate, maintain, and innovate transmission systems, ensuring vehicles remain reliable, efficient, and responsive in an ever-evolving world of mobility.
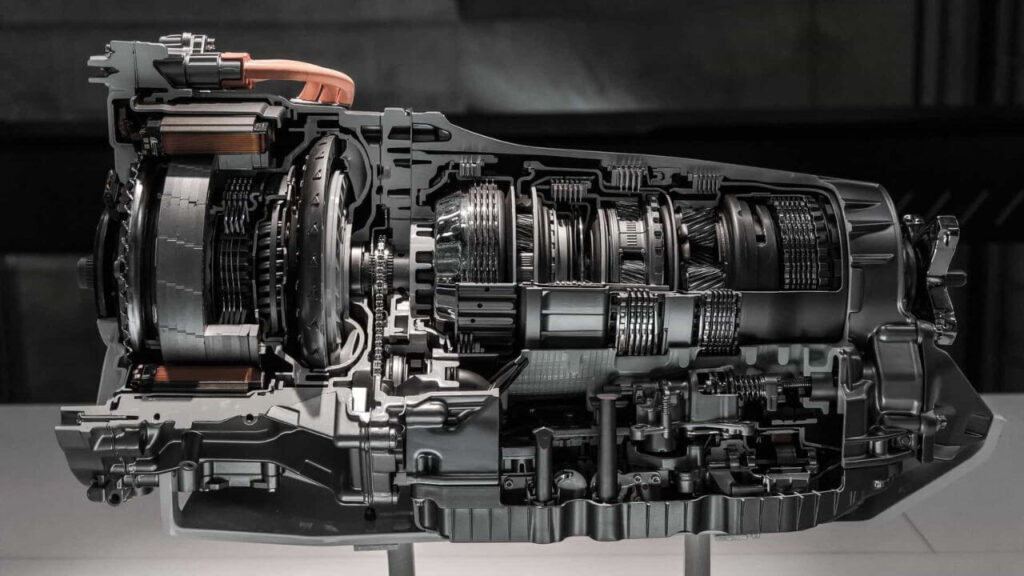


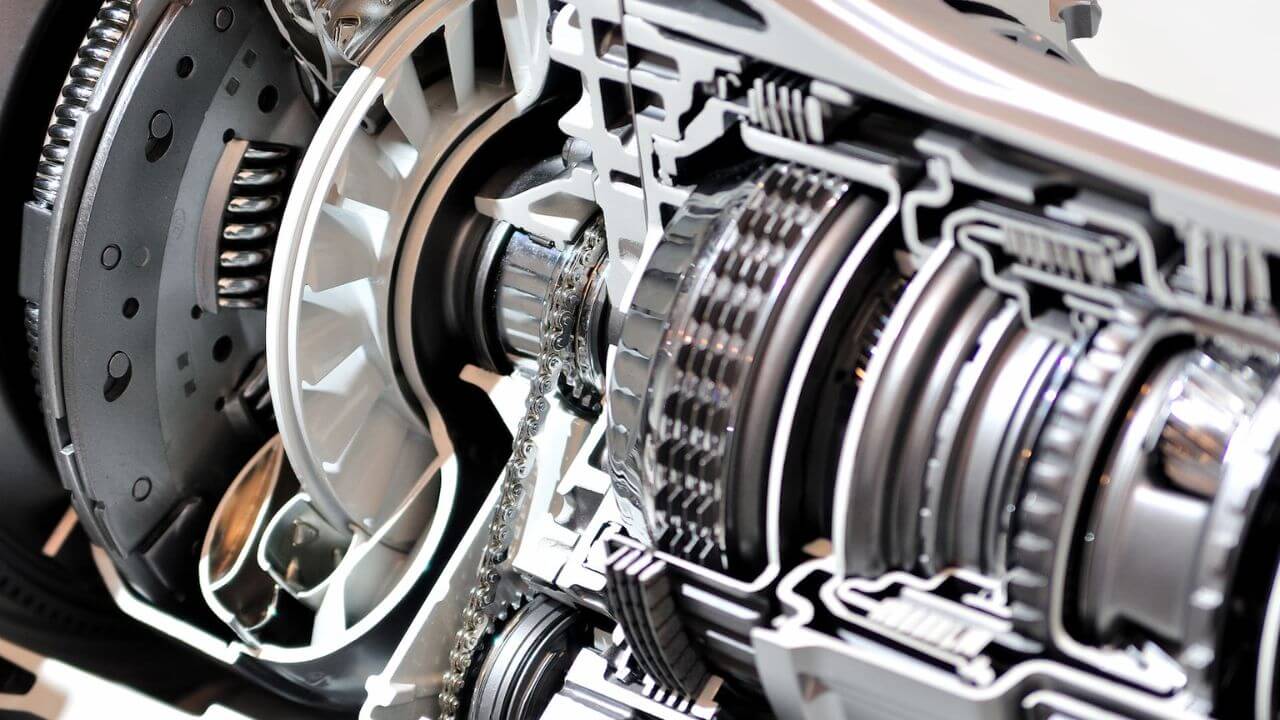 The Clutch: The Gateway to Power Activation
The Clutch: The Gateway to Power Activation