Explore the key differences between AWD vs FWD drivetrains to make an informed vehicle choice. Learn about performance, fuel efficiency, costs, and expert insights in this comprehensive guide.
When selecting a vehicle that meets one’s driving needs, the drivetrain is an important factor to consider. Many people hear the terms AWD vs FWD but are still confused as to which one would be best for their lifestyle. Both AWD and FWD have their unique pros and cons and are used for different driving conditions, budget and vehicle usage. This blog explores the intricacies of AWD vs. FWD, empowering readers to make well-informed choices with confidence and clarity.
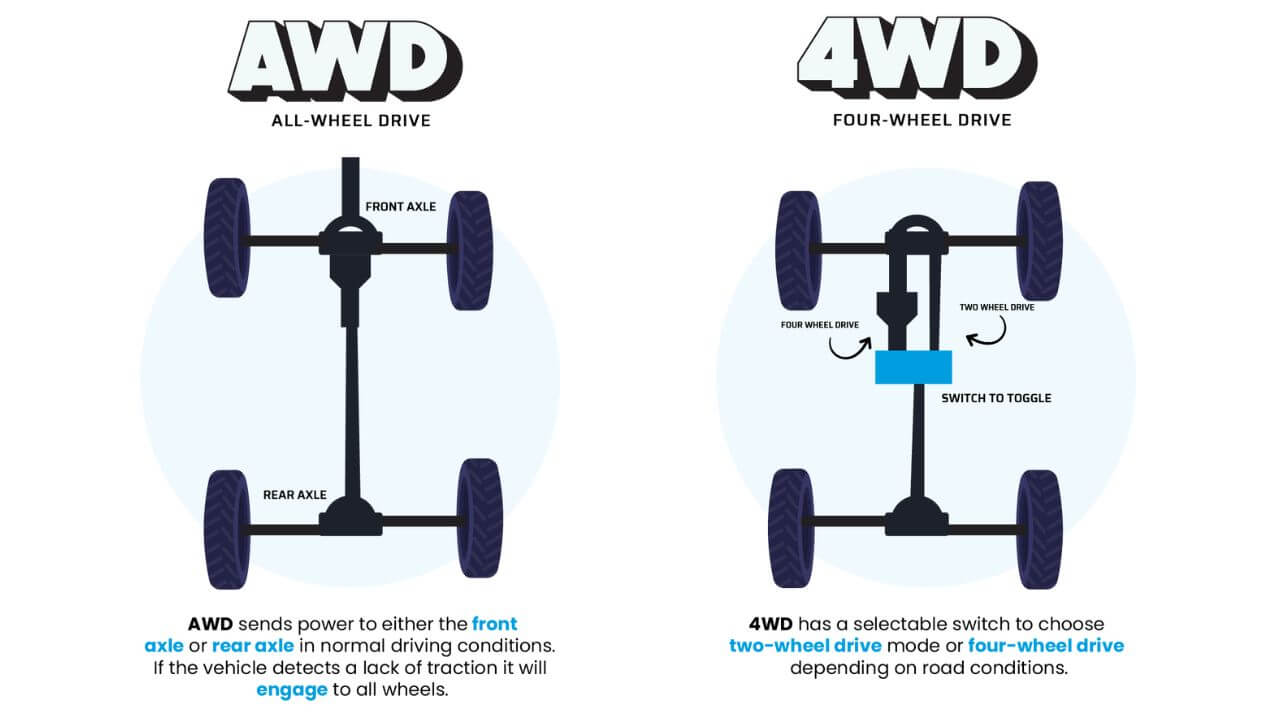
What Is AWD vs FWD?
On the other hand, FWD (Front-Wheel Drive) only transmits power from the engine to the front wheels. Such an arrangement is typical for a significant number of passenger vehicles and smaller-sized vehicles as it facilitates construction, reduces manufacturing cost, and enhances fuel economy. The front wheels are used for both propulsion (moving the car forward) and steering, so FWD is a sensible and economical option for day-to-day driving, particularly on paved roads.
How AWD and FWD Really Work
From a mechanical standpoint, the difference between AWD and FWD is how the power from the engine is transferred to the wheels. In a normal AWD system, sensors and computer controls transmit torque to each of the four wheels according to need for traction. This dynamic distribution ensures stability for the car even under demanding driving conditions such as snow, rain, or uneven terrain.
Whereas, FWD automobiles have all power sent to the front axle. Rather than having the engine and transmission via a driveshaft to the rear wheels, this system has a much simpler drivetrain configuration, thus making the system lighter and more fuel-efficient. The downside is that FWD vehicles are more likely to be skidding or sliding on slippery or uneven ground than their AWD counterparts.
Drivetrain Considerations in AWD vs FWD
The main benefit of AWD is its increased traction and control. Vehicles with AWD do an amazing job in bad weather (rain, snow, ice) and off-road situations where grip is critical. As all four wheels are powered, AWD helps to eliminate wheel slip and provides better acceleration and cornering control. This makes AWD a popular choice for drivers who need adaptability and safety in changing climates or different terrains.
On the other hand, FWD vehicles are designed for fuel economy and simplicity. Because of the fact that they only power the front wheels, FWD cars are lighter and usually get better gas mileage. The simpler drivetrain means less maintenance, which means less expense, attractive to a budget-conscious consumer. Furthermore, FWD usually offers better interior space, in that the drivetrain doesn’t intrude into the rear of the vehicle, which allows for greater cabin or cargo room.
So FWD does have some drawbacks. If the front wheels are the driving and steering wheels, and the vehicle is accelerate under hard acceleration or cornering, the wheels must carry both the steering and the power, and understeer (tendency to drive wide in corners) may result. In addition, FWD cars can have problems with traction on slippery slopes or loose surfaces.
Expert Opinion on AWD vs FWD
Dr. Emily Turner, automotive engineer, vehicle dynamics, explains:
Automotive drive wheels have the potential to provide a significant safety and driving confidence boost in inclement weather, but this is at the expense of increased complexity and fuel consumption. For the majority of urban drivers, FWD offers a good blend of efficiency and performance. Ultimately, the decision comes down to driving conditions and personal priorities.
This is because this expert insight sheds light on the trade-offs that users need to make and helps to put into perspective why AWD is favored for its ruggedness and FWD for its suitability for everyday commuting.
Social, Environmental, and Economic Impacts
Using a vehicle ownership cost approach, FWD vehicles are generally more economical both at the time of purchase and over time. They are also simpler mechanically, which means that they can be repaired and maintained less often, reducing operating costs. In addition, improved fuel efficiency means not only saving money but also generating a smaller environmental impact by lowering carbon emissions, a factor that has become a top concern in sustainability literature.
On the other hand, the AWD systems, while being more powerful in terms of traction, cause more fuel to be used. This increased weight and mechanical complexity means it has to spend more energy to do things, meaning it gets significantly fewer miles per gallon than FWD. The effect is most pronounced when AWD is always pushing all wheels for city driving and highway cruising.
Practical Applications: Where to Use AWD or FWD
So the AWD vs FWD decision should be based on the driver’s environment and lifestyle. For individuals residing in areas with regular snow, rain, or uneven road surfaces, AWD vehicles offer enhanced control and tranquility. This includes off-roaders, those that frequently drive on gravel or dirt roads, or frequently drive in inclement weather.
On the other hand, if most driving happens in cities or suburban areas, and road conditions are fairly predictable, FWD provides an excellent balance of fuel economy, cost and practicality. It’s especially ideal for households, commuters, and environmentally conscious drivers who prioritize affordability and reliability over versatility.
Key Differences Summarized
| Aspect | AWD | FWD |
|---|---|---|
| Power Distribution | Power to all four wheels | Power only to front wheels |
| Traction | Superior in snow, rain, rough terrain | Adequate for regular pavement |
| Fuel Efficiency | Lower due to added drivetrain components | Higher due to lighter setup |
| Maintenance Cost | Higher due to complexity | Lower, simpler design |
| Vehicle Cost | Generally higher initial purchase price | Usually more affordable |
| Handling Characteristics | Enhanced control on slippery surfaces | Tends toward understeer in sharp turns |
| Interior Space | Reduced due to mechanical components | More space for passengers/cargo |
Conclusion
In conclusion, mastering the knowledge of AWD vs FWD is an essential step in making an informed decision when purchasing a vehicle that suits one’s driving habits and expectations. Driving: AWD excels in confronting various challenging road conditions, providing an unmatched level of traction and safety, albeit at a premium cost and with increased fuel consumption. Meanwhile, FWD offers outstanding fuel economy, lower costs and real-world performance – especially for regular urban driving and mild weather.
This blog will aim to give readers a clear, comprehensive comparison that would help eliminate confusion in order to choose the right drivetrain for their needs. Whether it’s conquering rugged terrains or ensuring cost-effective efficiency, making the right choice allows for superior driving experiences and lasting satisfaction.
By considering factors like climate, driving style, budget, and vehicle purpose, prospective buyers can confidently make an informed decision between AWD and FWD, transforming their driving experience with knowledge and clarity.

